In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Semiconductor Alternating Current Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Question Alternating Current to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Alternating Current Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having a different number of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to the main supply of 120 V and the secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6Ω
(i) The value of voltage across the secondary coil is
| (a) 5V | (b) 2V | (c) 3 V | (d) 10 V |
Answer:(c) 3 V
(ii) The value of current in the bulb is
| (a) 7 A | (b) 15 A | (c) 3 A | (d) 5 A |
Answer:(d) 5 A
(iii) The value of current in the primary coil is
| (a) 0.125 A | (b) 2.52 A | (c) 1.51 A | (d) 3.52 A |
Answer:(a) 0.125 A
(iv) Power in primary coil is
| (a) 20W | (b) 5W | (c) 10 W | (d) 15W |
Answer:(d) 15W
(v) Power in secondary coil is
| (a) 15W | (b) 20 W | (c) 7W | (d) 8 W |
Answer:(a) 15W
Case Study 2:
When a pure resistance R, pure inductor L and an ideal capacitor of capacitance C is connected in series to a source of alternating e.m.f., then current at any instant through the three elements has the same amplitude and is represented as I = Iosinwt. However, voltage across each element has a different phase relationship with the current as shown in graph.
The effective resistance of RLC circuit is called impedance (2) of the circuit and the voltage leads the current by a phase angle ϕ.�.
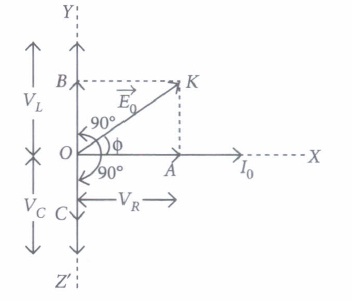
A resistor of 12Ω12Ω a capacitor of reactance 14Ω14Ω and a pure inductor of inductance 0.1 H are joined in series and placed across 200 V, 50 Hz a.c. supply
(i) The value of inductive reactance is
| (a) 15Ω | (b) 31.4Ω | (c) 20Ω | (d) 30Ω |
Answer: (b) 31.4Ω
(ii) The value of impedance is
| (a) 20Ω | (b) 15Ω | (c) 30Ω | (d) 21.13Ω |
Answer: (d) 21.13Ω
(iii) What is the value of current in the circuit?
| (a) 5 A | (b) 15 A | (c) 10 A | (d) 9.46 A |
Answer:(d) 9.46 A
(iv) What is the value of the phase angle between current and voltage?
| (a) 53∘9′ | (b) 63∘9′ | (c) 55∘4′ (c) 55∘4′ | (d) 50° |
Answer: (c) 55∘4
Case Study 3: Alternating Current, delves into the understanding of electrical currents that periodically reverse direction. The chapter starts by defining Alternating Current (AC) and contrasts it with Direct Current (DC), which flows in a single direction. AC is characterized by its frequency, which is the number of cycles per unit of time, and by its peak and RMS values. The chapter also explores the concept of impedance, which is a measure of opposition to AC, similar to the concept of resistance in DC circuits. Phasor diagrams are introduced to represent the phase difference between voltage and current in an AC circuit.
How is Alternating Current (AC) different from Direct Current (DC)?
A) AC flows in a single direction, while DC periodically reverses direction.
B) AC periodically reverses direction, while DC flows in a single direction.
C) Both AC and DC periodically reverse direction.
D) Both AC and DC flow in a single direction.
What characterizes Alternating Current?
A) Its frequency, peak and RMS values.
B) Its resistance and impedance.
C) Its current and voltage.
D) Its direction and amplitude.
What is impedance in an AC circuit?
A) A measure of the flow of AC.
B) A measure of opposition to AC.
C) A measure of the direction of AC.
D) A measure of the frequency of AC.
What is a phasor diagram used for?
A) To represent the direction of AC.
B) To represent the frequency of AC.
C) To represent the phase difference between voltage and current in an AC circuit.
D) To represent the resistance and impedance in an AC circuit.
What is resonance in an AC circuit?
A) The condition where the frequency of the AC equals the natural frequency of the circuit.
B) The condition where the impedance of the AC equals the resistance of the circuit.
C) The condition where the voltage of the AC equals the current of the circuit.
D) The condition where the direction of the AC equals the direction of the DC.
Answers:
- B) AC periodically reverses direction, while DC flows in a single direction.
- A) Its frequency, peak and RMS values.
- B) A measure of opposition to AC.
- C) To represent the phase difference between voltage and current in an AC circuit.
- A) The condition where the frequency of the AC equals the natural frequency of the circuit.
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 12 Physics Alternating Current Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate

