In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: When the diode is forward biased, it is found that beyond forward voltage V = Vk, called knee voltage, the conductivity is very high. At this value of battery biasing for the p-n junction, the potential barrier is overcome, and the current increases rapidly with an increase in forwarding voltage. When the diode is reverse biased, the reverse bias voltage produces a very small current of about a few microamperes which almost remains constant with bias. This small current is a reverse saturation current.
In which of the following figures, the p-n diode is forward biased

Answer:(d) : All options are basic properties of nuclear forces. So, all options are correct.
Based on the V-I characteristics of the diode, we can classify diode as
(a) bi-directional device
(b) ohmic device
(c) non-ohmic device
(d) passive element
Answer:(d) passive element
The V-I characteristic of a diode is shown in the figure. The ratio of forward to reverse bias resistance is

(a) 100 (b) 106 (c) 10 (d) 10–6
Answer:(d) 10–6
In the case of forwarding biasing of a p-n junction diode, which one of the following figures correctly depicts the direction of conventional current (indicated by an arrow mark)?

Answer:(a)
If an ideal junction diode is connected as shown, then the value of the current I is
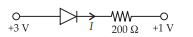
(a) 0.013 A (b) 0.02 A
(c) 0.01 A (d) 0.1 A
Answer:(a)0.013 A
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 2: A photodiode is an optoelectronic device in which current carriers are generated by photons through photo-excitation i.e., photoconduction by light. It is a p-n junction fabricated from a photosensitive semiconductor and provided with a transparent window so as to allow light to fall on its junction. A photodiode can turn its current ON and OFF in nanoseconds. So, it can be used as the fastest photo-detector

The photodiode is a device
(a) that is always operated in reverse bias.
(b) which is always operated in forwarding bias.
(c) in which photocurrent is independent of the intensity of incident radiation.
(d) which may be operated in both forward or reverse bias
Answer:(a) that is always operated in reverse bias.
To detect light of wavelength 500 nm, the photodiode must be fabricated from a semiconductor of a minimum bandwidth of
(a) 1.24 eV (b) 0.62 eV
(c) 2.48 eV (d) 3.2 eV
Answer:(c) 2.48 eV
The photodiode can be used as a photodetector to detect
(a) optical signals (b) electrical signals
(c) both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
Answer:(b) electrical signals
Case Study 3: Chapter 14, Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits, explains the properties and applications of semiconductors. It begins by defining semiconductors, materials with electrical conductivity between that of conductors and insulators. The chapter discusses two main types of semiconductors: intrinsic (pure) and extrinsic (impure). Extrinsic semiconductors are further categorized into n-type and p-type based on the type of impurities added. It introduces diodes, which allow current to flow only in one direction, and transistors, which are crucial for amplification and switching. Finally, it delves into simple circuits, explaining the role of these semiconductor devices in rectification, filtering, and voltage regulation.
How is the electrical conductivity of semiconductors described?
A) It is higher than that of conductors and insulators.
B) It is lower than that of conductors and insulators.
C) It is between that of conductors and insulators.
D) It is equal to that of conductors.
What are the two main types of semiconductors?
A) Metals and non-metals
B) Solids and gases
C) Intrinsic and extrinsic
D) Positive and negative
What are n-type and p-type semiconductors?
A) They are types of intrinsic semiconductors.
B) They are types of extrinsic semiconductors.
C) They are types of conductors.
D) They are types of insulators.
What is the primary function of a diode?
A) To allow current to flow in both directions.
B) To prevent current from flowing.
C) To allow current to flow only in one direction.
D) To transform AC current into DC current.
What role do semiconductors play in simple circuits?
A) They store energy.
B) They produce light.
C) They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
D) They play a role in rectification, filtering, and voltage regulation.
Answers:
C) It is between that of conductors and insulators.
C) Intrinsic and extrinsic
B) They are types of extrinsic semiconductors.
C) To allow current to flow only in one direction.
D) They play a role in rectification, filtering, and voltage regulation.
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 12 Physics Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, and Simple Circuits Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate

