In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions Wave Optics to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Wave Optics Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1:Huygen principle is the basis of the wave theory of light. Each point on a wavefront acts as a fresh source of new disturbance, called secondary waves or wavelets. The secondary wavelets spread out in all directions with the speed of light in the given medium. An initially parallel cylindrical beam travels in a medium of refractive index u(I) = u0 + u2I, where u0 and u2 are positive constants and I is the intensity of the light beam. The intensity of the beam is decreasing with increasing radius.

The initial shape of the wavefront of the beam is
(a) planar (b) convex
(c) concave
(d) convex near the axis and concave near the periphery
Answer: (a): As the beam is initially parallel, the shape of wavefront is planar.
According to Huygens Principle, the surface of constant phase is
(a) called an optical ray (b) called a wave
(c) called a wavefront
(d) always linear in shape
Answer: (c) : According to Huygens Principle, the surface of constant phase is called a wavefront.
As the beam enters the medium, it will
(a) travel as a cylindrical beam
(b) diverge
(c) converge
(d) diverge near the axis and converge near the periphery
Answer: (c) converge
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 2:The phenomenon of bending of light around the sharp corners and the spreading of light within the geometrical shadow of the opaque obstacles is called the diffraction of light. The light thus deviates from its linear path. The deviation becomes much more pronounced when the dimensions of the aperture or the obstacle is comparable to the wavelength of light.
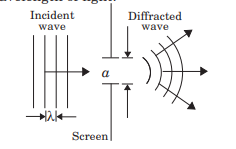
In diffraction from a single slit the angular width of the central maxima does not depend on
(a) l of light used
(b) width of slit
(c) distance of slits from the screen
(d) the ratio of l and slit width
Answer:(c) distance of slits from the screen
For diffraction from a single slit, the intensity of the central point is
(a) infinite
(b) finite and same magnitude as the surrounding maxima
(c) finite but much larger than the surrounding maxima
(d) finite and substantially smaller than the surrounding maxima
Answer:(c) finite but much larger than the surrounding maxima
In a single diffraction pattern observed on a screen placed at D metre distance from the slit of width d metre, the ratio of the width of the central maxima to the width of other secondary maxima is
(a) 2 : 1 (b) 1 : 2 (c) 1 : 1 (d) 3 : 1
Answer:(a) 2 : 1
Case Study 3: Chapter 10, Wave Optics, presents the wave theory of light, focusing on the principles of interference, diffraction, and polarization. A crucial concept in this chapter is the Huygens Principle, which states that every point on a wavefront can be considered a source of secondary wavelets. These wavelets spread out in all directions at the same speed as that of the original wave. Interference is another key principle covered. It refers to the phenomenon that occurs when two waves combine to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Young’s Double Slit Experiment provided the first conclusive proof of the wave nature of light by demonstrating this interference principle. Finally, polarization, a property that distinguishes transverse waves from longitudinal waves, is a phenomenon exclusive to waves that can oscillate in more than one direction.
What does the Huygens Principle state?
A) Every point on a wavefront is a source of secondary wavelets, which spread out in all directions with the speed of the original wave.
B) Every point on a wavefront is a source of primary wavelets, which spread out in one direction with the speed of the original wave.
C) Every point on a wavefront is a source of secondary wavelets, which spread out in all directions with double the speed of the original wave.
D) Every point on a wavefront absorbs secondary wavelets.
What is the phenomenon that occurs when two waves combine to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude?
A) Diffraction
B) Reflection
C) Refraction
D) Interference
Which experiment provided the first conclusive proof of the wave nature of light?
A) Young’s Double Slit Experiment
B) Huygens Principle Experiment
C) Einstein’s Photoelectric Effect Experiment
D) Michelson-Morley Experiment
What property distinguishes transverse waves from longitudinal waves?
A) Wavelength
B) Amplitude
C) Frequency
D) Polarization
What is a phenomenon exclusive to waves that can oscillate in more than one direction?
A) Diffraction
B) Polarization
C) Interference
D) Reflection
Answers:
- A) Every point on a wavefront is a source of secondary wavelets, which spread out in all directions with the speed of the original wave.
- D) Interference
- A) Young’s Double Slit Experiment
- D) Polarization
- B) Polarization
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about the CBSE Class 12 Physics Wave Optics Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate

