In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Case Study Questions Coordination Compounds to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Coordination Compounds Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the IUPAC system. A few rules for naming coordination compounds are :
(I) In the ionic complex, the cation is named first and then the anion.
(II) In the coordination entity, the ligands are named first and then the central metal ion.
(III)When more than one type of ligands are present, they are named in alphabetical order of preference without any consideration of charge
The IUPAC name of the complex [Pt(NH3)3Br(NO2)Cl]Cl is
(a) triamminechlorobromonitroplatinum(IV) chloride
(b) triamminebromonitrochloroplatinum(IV) chloride
(c) triamminebromidochloridonitroplatinum (IV) chloride
(d) triamminenitrochlorobromoplatinum(IV) chloride
Answer:(c) triamminebromidochloridonitroplatinum (IV) chloride
The IUPAC name of [Ni(CO)4] is
(a) tetracarbonylnickel(II)
(b) tetracarbonylnickel(0)
(c) tetracarbonylnickelate(II)
(d) tetracarbonylnickelate(0).
Answer:(b) tetracarbonylnickel(0)
As per IUPAC nomenclature, the name of the complex [Co(H2O)4(NH3)2]Cl3 is
(a) tetraaquadiamminecobalt(II) chloride
(b) tetraaquadiamminecobalt(III) chloride
(c) diamminetetraaquacobalt(II) chloride
(d) diamminetetraaquacobalt(III) chloride.
Answer:(d) diamminetetraaquacobalt(III) chloride.
Which of the following represents the correct formula of dichloridobis(ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt(III) ion?
(a) [CoCl2(en)]2+ (b) [CoCl2(en)2] 2+
(c) [CoCl2(en)]+ (d) [CoCl2(en)2]+
Answer: (d) [CoCl2(en)2]+
Correct formula of pentaamminenitrito-Ocobalt(III) sulphate is
(a) [Co(NO2)(NH3)5]SO4
(b) [Co(ONO)(NH3)5]SO4
(c) Co(NO2)(NH3)4( SO4 )2
(d) Co(ONO)(NH3)4( SO4 )2
Answer: (b) [Co(ONO)(NH3)5]SO4
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 2: To explain bonding in coordination compounds various theories were proposed. One important theory was the valence bond theory. According to that, the central metal ion in the complex makes available a number of empty orbitals for the formation of coordination bonds with suitable ligands. The appropriate atomic orbitals of the metal hybridize to give a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry.
The d-orbitals involved in the hybridization may be either inner d-orbitals i.e., (n – 1)d, or outer d-orbitals i.e., nd. For example, Co3+ forms both inner orbital and outer orbital complexes, with ammonia forms [Co(NH3)6]3+ and with fluorine it forms [CoF6]3– complexion.
Which of the following is not true for [CoF6]3–?
(a) It is paramagnetic.
(b) It has coordination number of 6.
(c) It is an outer orbital complex.
(d) It involves d2sp3 hybridization.
Answer: (d) It involves d2sp3 hybridization.
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (at. no. of Cr = 24) has a magnetic moment of 3.83 B.M. The correct distribution of 3d-electrons in the central metal of the complex is
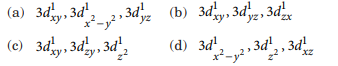
Answer: (b)
Which of the following is true for[Co(NH3)6]3+?
(a) It is an octahedral, diamagnetic, and outer orbital complex.
(b) It is an octahedral, paramagnetic, and outer orbital complex.
(c) It is an octahedral, paramagnetic, and inner orbital complex.
(d) It is an octahedral, diamagnetic, and inner orbital complex
Answer: (d) It is an octahedral, diamagnetic, and inner orbital complex
The paramagnetism of [CoF6]3– is due to
(a) 3 electrons (b) 4 electrons
(c) 2 electrons (d) 1 electron.
Answer: (b) 4 electrons
Which of the following is an inner orbital or low spin complex?
(a) [Ni(H2O)6]3+ (b) [FeF6]3–
(c) [Co(CN)6]3– (d) [NiCl4]2–
Answer: (c) [Co(CN)6]3–
Case Study 3: The molecular compounds which are formed from the combination of two or more simple stable compounds and retain their identity in the solid as well as in the dissolved state are called coordination compounds. Their properties are completely different from their constituents. In coordination compounds, the central metal atom or ion is linked to a number of ions or neutral molecules, called ligands, by coordinate bonds. For example, Dimethyl glyoxime (dmg) is a bidentate ligand chelating large amounts of metals. When dimethyl glyoxime is added to an alcoholic solution of NiCl2 and ammonium hydroxide is slowly added to it, a rosy red precipitate of a complex is formed.
(i) The structure of the complex is
(ii) Oxidation number of Ni in the given complex is
| (a) +3 | (b) +1 | (c) +2 | (d) zero. |
(iii) Which of the following is true about this complex?
| (a) It is paramagnetic, containing 2 unpaired electrons. |
| (b) It is paramagnetic, containing 1 unpaired electron. |
| (c) It is paramagnetic, containing 4 unpaired electrons. |
| (d) It is diamagnetic with no unpaired electron |
(iv) Which one will give test for Fe3+ ions in the solution?
| (a) [Fe(CN)6]3- | (b) [Fe(CN)6]2- |
| (c) (NH4)2SO4· FeSO4· 6H2O | (d) Fe2(SO4)3 |
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate

