In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Case Study Questions Surface Chemistry to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Surface Chemistry Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: A graph between the amount adsorbed (x/m) by an adsorbent and the equilibrium pressure of the adsorbate at a constant temperature is called the adsorption isotherm. A relationship between the amount adsorbed (x/m) and the equilibrium pressure (P) can be obtained as follows :
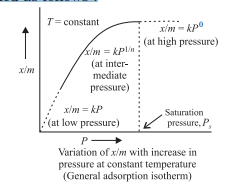
In the intermediate range of pressure, x/m = kP1/n (was originally put forward by Freundlich and is known as Freundlich adsorption isotherm).
According to Freundlich adsorption isotherm, which of the following is correct?
(a) x/m ∝ P0
(b) x/m ∝ P1
(c) x/m ∝ P1/n
(d) All the above are correct for different ranges of pressure.
Answer: (d) All the above are correct for different ranges of pressure.
In the Freundlich adsorption isotherm equation
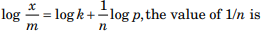
(a) any value from 0 to 1
(b) a negative integer
(c) a positive integer
(d) a positive or a negative fractional number.
Answer: (a) any value from 0 to 1
The plot of log x/m against log p is a straight line inclined at an angle of 45°. When the pressure is 0.5 atm and Freundlich parameter, k is 10, the amount of solute adsorbed per gram of adsorbent will be (log 5 = 0.6990)
(a) 1 g (b) 2 g
(c) 3 g (d) 5 g
Answer: (d) 5 g
In the plot of log x/m vs log p for adsorption, a straight line inclined at an angle of q = 14.04° to the x-axis was obtained. The ‘n’ value for this adsorption process is (tan 14.04° = 0.25)
(a) 5 (b) 8
(c) 4 (d) 2
Answer: (c) 4
In the adsorption of a gas on solid, Freundlich isotherm is obeyed. The slope of the plot is zero. Then the extent of adsorption is
(a) directly proportional to the pressure of the gas
(b) inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas
(c) directly proportional to the square root of the pressure of the gas
(d) independent of the pressure of the gas
Answer: (d) independent of the pressure of the gas
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 2:Adsorption is a spontaneous process and involves the unequal distribution of the molecules of the gaseous substance on the surface of a solid or liquid. Adsorption is an exothermic process. The attractive forces between adsorbate and adsorbent are either van der Waals’ forces or chemical bonds. The adsorption of gases on solids is generally controlled by factors like temperature, pressure, and the nature of adsorbate and adsorbent.
In the physisorption process, the attractive forces between adsorbate and adsorbent are
(a) covalent bonds
(b) ionic bonds
(c) van der Waals’ forces
(d) H-bonds
Answer: (c) van der Waals’ forces
Which of the following graph represents the variation of physical adsorption with temperature?

Answer: (a)
Which one of the following processes does not use adsorption?
(a) Froth floatation process
(b) Chromatography
(c) Decolourisation of sugar liquors
(d) Dissolution of sugar in water
Answer: (d) Dissolution of sugar in water
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Chemisorption forms an unimolecular layer.
(b) Chemisorption is a reversible process.
(c) Chemisorption is independent of pressure.
(d) Chemisorption has low enthalpy change.
Answer: (a) Chemisorption forms an unimolecular layer.
Methylene blue, from its aqueous solution, is adsorbed on activated charcoal at 25°C. For this process, the correct statement is
(a) the adsorption requires activation at 25°C
(b) the adsorption is accompanied by a decrease in enthalpy
(c) the adsorption increases with the increase of temperature
(d) the adsorption is irreversible
Answer: (b) the adsorption is accompanied by a decrease in enthalpy
Case Study 3: Adsorption depends on the nature of the adsorbent. The rough solid surface has more pores and adsorbs more gases than the smooth surface. The most common adsorbents are silica gel, and activated charcoal The extent of adsorption also depends on the surface area of the solid. The specific surface area of an adsorbent is the surface area available for adsorption per gram of the adsorbent. The greater the surface area of the solid, the greater would be the adsorption. Charcoal is a more effective adsorbent than solid wood. Desorption is the process of removing an adsorbed substance from a surface on which it is absorbed.
Physisorption is non-specific and any gas can be adsorbed. But the gases which are easily liquefiable (e.g., NH3, HCl, CO2 ) are adsorbed at a faster rate and to a large extent than the gases which are difficult to liquefy (e.g., H2, O2, N2 ). It depends on the critical temperature. Higher the critical temperature of a gas, the more easily liquefiable the gas is and the more is the rate of adsorption. Chemisorption is specific in nature. Therefore, only those gases can be adsorbed which are capable of forming chemical bonds with the adsorbent.
(i) Select the correct statement regarding desorption.
| (a) It is done by cooling or by increasing the pressure applied. |
| (b) It is done by cooling or by reducing the pressure applied. |
| (c) It is done by heating or by reducing the pressure applied |
| (d) It is done by heating or by increasing the pressure applied. |
Answer: (c) It is done by heating or by reducing the pressure applied
(ii) Which of the following statements regarding the physical adsorption of a gas on surface of solid is not correct?
| (a) On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously |
| (b) Enthalpy changes are negative |
| (c) It is non-specific in nature |
| (d) It is reversible in nature |
Answer: (a) On increasing temperature, adsorption increases continuously
(iii) At the same temperature and pressure, select the correct order of adsorption of the following gases on the same mass of charcoal.
| (a) SO2 > CH4 > H2 | (b) CH4 < SO2 < H2 |
| (c) Hz > CH4 > SO2 | (d) CH4 < H2 < SO2 |
Answer: (a) SO2 > CH4 > H2
(iv) Select the incorrect statement among the following.
| (a) Physical adsorption occurs at a low temperature and chemisorption occurs at all temperature |
| (b) In physisorption heat of adsorption is low while in chemisorption it is high |
| (c) Chemisorption is irreversible and physisorption is reversible |
| (d) Magnitude of chemisorption decreases with rise in temperature while physisorption increases with rise in temperature. |
Answer: (d) Magnitude of chemisorption decreases with rise in temperature while physisorption increases with rise in temperature.
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Surface Chemistry Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate



