In Class 11 Final Exams there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve Class 11 Physics Case Study Question Oscillations to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 11 Physics Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Oscillations Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Oscillations
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Case Study 1: Simple Harmonic Motion – Simple harmonic motion is the simplest form of oscillation. A particular type of periodic motion in which a particle moves to and fro repeatedly about a mean position under the influence of a restoring force is termed simple harmonic motion (S.H.M). A body is undergoing simple harmonic motion if it has an acceleration that is directed towards a fixed point, and proportional to the displacement of the body from that point.
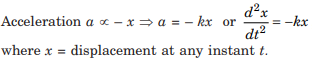
Which of the following is not a characteristic of simple harmonic motion?
(a) The motion is periodic.
(b) The motion is along a straight line about the mean position.
(c) The oscillations are responsible for the energy conversion.
(d) The acceleration of the particle is directed towards the extreme position.
Answer: (d) The acceleration of the particle is directed towards the extreme position.
The equation of motion of a simple harmonic motion is
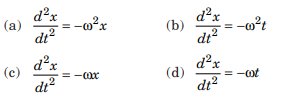
Answer: (a)
Which of the following expressions does not represent simple harmonic motion?
(a) x = Acoswt + Bsinwt(b) x = Acos(wt + a)
(c) x = Bsin(wt + b) (d) x = Asinwt cos2wt
Answer: (d) x = Asinwt cos2wt
The time period of simple harmonic motion depends upon
(a) amplitude (b) energy
(c) phase constant (d) mass
Answer: (d) mass
Which of the following motions is not simple harmonic?
(a) Vertical oscillations of a spring
(b) Motion of a simple pendulum
(c) Motion of planet around the Sun
(d) Oscillation of liquid in a U-tube
Answer: (c) Motion of planet around the Sun
Case Study 2: When a system (such as a simple pendulum or a block attached to a spring) is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it oscillates with its natural frequency ω, and the oscillations are called free oscillations. All free oscillations eventually die out because of the ever-present damping forces. However, an external agency can maintain these oscillations. These are called forced or driven oscillations. We consider the case when the external force is itself periodic, with a frequency wd called the driven frequency. The most important fact of forced periodic oscillations is that the system oscillates not with its natural frequency ω, but at the frequency ωd of the external agency; the free oscillations die out due to damping. The most familiar example of forced oscillation is when a child in a garden swing periodically presses his feet against the ground (or someone else periodically gives the child a push) to maintain the oscillations. The maximum possible amplitude for a given driving frequency is governed by the driving frequency and the damping and is never infinity. The phenomenon of increase in amplitude, when the driving force is close to the natural frequency of the oscillator, is called resonance. In our daily life, we encounter phenomena that involve resonance. Your experience with swings is a good example of resonance. You might have realized that the skill of swinging to greater heights lies in the synchronization of the rhythm of pushing against the ground with the natural frequency of the swing.
What are the oscillations called when a system is displaced from its equilibrium position and released?
a) Damped oscillations
b) Forced oscillations
c) Free oscillations
d) Resonant oscillations
Answer: c) Free oscillations
What happens to free oscillations due to the presence of damping forces?
a) They increase in frequency
b) They increase in amplitude
c) They eventually die out
d) They continue indefinitely
Answer: c) They eventually die out
In forced oscillations, at what frequency does the system oscillate?
a) At its natural frequency ω
b) At the frequency ωd of the external agency
c) At the resonance frequency
d) At the damping frequency
Answer: b) At the frequency ωd of the external agency
What is the term for the phenomenon where the amplitude increases when the driving force is close to the natural frequency of the oscillator?
a) Damping
b) Oscillation
c) Resonance
d) Harmonics
Answer: c) Resonance
What is one of the most familiar examples of forced oscillation?
a) The movement of a plucked guitar string
b) The motion of a pendulum clock
c) A child in a garden swing periodically pressing his feet against the ground
d) The orbit of a planet around a star
Answer: c) A child in a garden swing periodically pressing his feet against the ground
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Oscillations with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about the CBSE Class 11 Physics Oscillations Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate


