In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions Nuclei to know their preparation level.
In CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Nuclei Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: The nucleus was first discovered in 1911 by Lord Rutherford and his associates by experiments on the scattering of a-particles by atoms. He found that the scattering results could be explained if atoms consist of a small, central, massive, and positive core surrounded by orbiting electrons. The experimental results indicated that the size of the nucleus is of the order of 10–14 m and is thus 10000 times smaller than the size of an atom.
The ratio of the mass of the nucleus to a mass of an atom is approximately
(a) 1 (b) 10
(c) 103 (d) 1010
Answer: (a) 1
Masses of nuclei of hydrogen, deuterium, and tritium are in the ratio
(a) 1 : 2 : 3 (b) 1 : 1 : 1
(c) 1 : 1 : 2 (d) 1 : 2 : 4
Answer: (a) 1 : 2 : 3
Nuclides with the same neutron number but different atomic numbers is
(a) isobars (b) isotopes
(c) isotones (d) none of these
Answer: (c) isotones
If R is the radius and A is the mass number, then log R versus log A graph will be
(a) a straight line (b) a parabola
(c) an ellipse (d) None of these
Answer: (a) a straight line
The ratio of the nuclear radii of the mercury isotope 198 80Hg and silver isotope 107 47Ag is
(a) 1.23 (b) 0.216
(c) 2.13 (d) 3.46
Answer: (a) 1.23
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 2: In the year 1939, German scientists Otto Hahn and Strassmann discovered that when a uranium isotope was bombarded with a neutron, it breaks into two intermediate mass fragments. It was observed that the sum of the masses of new fragments formed was less than the mass of the original nuclei. This difference in the mass appeared as the energy released in the process. Thus, the phenomenon of splitting a heavy nucleus (usually A > 230) into two or lighter nuclei by the bombardment of the proton, neutron, a-particle, etc with the liberation of energy is called nuclear fission.
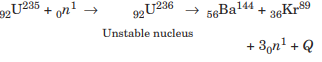
Nuclear fission can be explained on the basis of
(a) Millikan’s oil drop method
(b) Liquid drop model
(c) Shell model
(d) Bohr’s model
Answer: (b) Liquid drop model
For sustaining the nuclear fission chain reaction in a sample (of small size) of 235 92U, it is desirable to slow down fast neutrons by
(a) friction
(b) elastic damping/scattering
(c) absorption
(d) cooling
Answer: (b) elastic damping/scattering
On average, the number of neutrons and the energy of a neutron released per fission of a uranium atom are respectively
(a) 2.5 and 2 keV (b) 3 and 1 keV
(c) 2.5 and 2 MeV (d) 2 and 2 keV
Answer: (c) 2.5 and 2 MeV
In any fission process, the ratio of the mass of the daughter nucleus to the mass of the parent nucleus is
(a) less than 1
(b) greater than 1
(c) equal to 1
(d) depends on the mass of parent nucleus
Answer: (a) less than 1
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 3: Neutrons and protons are identical particles in the sense that their masses are nearly the same and the force, called nuclear force, does distinguish them. The nuclear force is the strongest force. The stability of the nucleus is determined by the neutron-proton ratio mass defect or packing fraction. The shape of the nucleus is calculated by quadrupole moment and the spin of the nucleus depends on even or odd mass numbers. The volume of the nucleus depends on the mass number. The whole mass of the atom (nearly 99%) is centered at the nucleus
The correct statements about the nuclear force is/are
(a) charge independent
(b) short range force
(c) non-conservative force
(d) all of these
Answer: (d) all of these
A force between two protons is the same as the force between proton and neutron. The nature of the force is
(a) electrical force (b) weak nuclear force
(c) gravitational force (d) strong nuclear force
Answer: (d) strong nuclear force
All the nucleons in an atom are held by
(a) nuclear forces
(b) Van der Waal’s forces
(c) tensor forces
(d) coulomb forces
Answer: (a) nuclear forces
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about the CBSE Class 13 Physics Nuclei Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible.
By Team Study Rate

